√ダウンロード p(x 2) binomial distribution 292220-How to find p(x) in binomial distribution
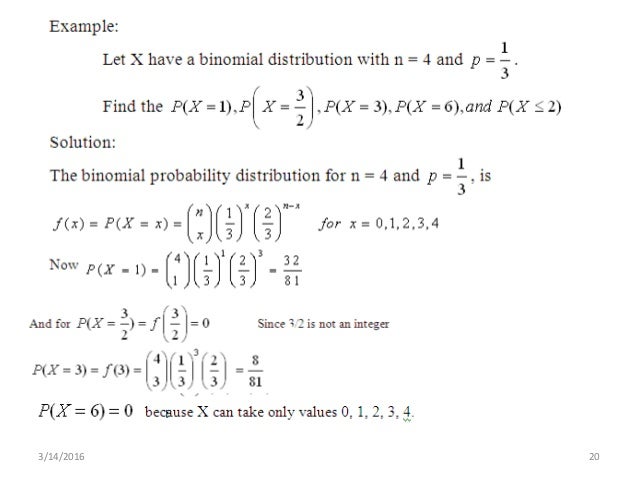
Characteristics of binominal distribution A random variable has a binomial distribution if met this following conditions 1 There are fixed numbers of trials (n) 2 Every trial only has two possible results success or failure 3 The probability of success for each trial is always equal Usually, the success one symbolized with (p) 4If we assume the probabilities of each of the values is equal, then the probability would be \(P(X=2)=\frac{1}{5}\) We can define the probabilities of each of the outcomes using the probability mass function (PMF) described in the last section Here, the number of redflowered plants has a binomial distribution with \(n = 5, p = 025If we assume the probabilities of each of the values is equal, then the probability would be \(P(X=2)=\frac{1}{5}\) We can define the probabilities of each of the outcomes using the probability mass function (PMF) described in the last section Here, the number of redflowered plants has a binomial distribution with \(n = 5, p = 025
4 Discrete Rand Vars
How to find p(x) in binomial distribution
How to find p(x) in binomial distribution-Hence the probability of throwing 2 heads and 8 tails is 10 C 2 × (½) 2 × (½) 8 As you can see this has a Binomial distribution, where n = 10, p = ½ You can see, therefore, that the pdf is going to be P(X = x) = 10 C x (½) (10x) (½) x From this, we can work out the probability of throwing, for example, 3 heads (put x = 3) ThisAnswer Using the Binomial Distribution Calculator above with p = 05, n = 5, and k = 2, we find that P(X≤2) = 05 Problem 3 Question The probability that a given student gets accepted to a certain college is 02


3
The Binomial Distribution The binomial distribution is a special discrete distribution where there are two distinct complementary outcomes, a "success" and a "failure"Balbharati solutions for Mathematics and Statistics 2 (Arts and Science) 12th Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 8 (Binomial Distribution) include all questions with solution and detail explanation This will clear students doubts about any question and improve application skills while preparing for board exams The detailed, stepbystep solutions will help you understand theThe probability of finding a defective item is p Binomial distribution could be represented as B(30,p) A person suffering from a disease Probability of finding 0 or more number of people suffering from a particular disease while examining 100 people;
The word "binomial" literally means "two numbers"A binomial distribution for a random variable X (known as binomial variate) is one in which there are only two possible outcomes, success and failure, for a finite number of trials Note that however we define success and failure, the two events must be mutually exclusive and complementary;Binomial distribution was discovered by James Bernoulli () in the year 1700 qnd was first published posthumously in 1713, eight years after his death Let a random experiment be performed repeatedly, each repitition being called a trial and let the occurrence of an event in a trial be called a success and its nonoccurrence a failure= x(x1)(x2)1, and 0!
Binomial Random Variables In general, the probability mass function (pmf) of a Binomial RV can be written as p X (x) = (n x) p x (1p) nx for x = 0, 1, 2, , n 0 otherwise • Cumulative distribution function (cdf) F X (t) = P (X ≤ t) = b t c X x =0 n x p x (1p) nx (Add up the pmfs to obtain the cdf) • Expected Value E (X) = np= 1) E(X) = np = 3* 03 = 09 P(X=x)=!( )!!Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\) Suppose a random variable, x, arises from a binomial experimentSuppose n = 6, and p = 013 Write the probability distribution Draw a histogram Describe the shape of the histogram


The Mean And Variance Of A Binomial Variate X With The Parameters N And P Are 16 And 8 Respectively What Is The Probability Of The Event X 2 Quora



Binomial Distribution Real Statistics Using Excel
The Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution with = 3 The kurtosis goes to infinity for high and low values of p , {\displaystyle p,} but for p = 1 / 2 {\displaystyle p=1/2} the twopoint distributions including the Bernoulli distribution have a lower excess kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namelyWhere $ ( {} _ {x} ^ {n} ) $ is the binomial coefficient, and $ p $ is a parameter of the binomial distribution, called the probability of a positive outcome, which can take values in the interval $ 0 \leq p \leq 1 $Bernoulli distribution The Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution, where n = 1 Symbolically, X ~ B(1, p) has the same meaning as X ~ Bernoulli(p)Conversely, any binomial distribution, B(n, p), is the distribution of the sum of n Bernoulli trials, Bernoulli(p), each with the same probability pPoisson binomial distribution


Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template



Binomial Distribution Calculator
P(X ≤ 2) = 1/32 5/32 = 3/16 Practice Problems Solve the following problems based on binomial distribution The mean and variance of the binomial variate X are 8 and 4 respectively Find P(XP k (1p) (nk) Like this (to 4 decimal places) P(X = 0) = 4!0!4!Answer Using the Binomial Distribution Calculator above with p = 05, n = 5, and k = 2, we find that P(X≤2) = 05 Problem 3 Question The probability that a given student gets accepted to a certain college is 02


Solved Problem Statement The Binomial Distribution Consists Of The Probabilities Of Each Of The Possible Numbers Of Successes X On N Trials For Ind Course Hero



The Binomial Distribution
Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeTo find probabilities from a binomial distribution, one may either calculate them directly, use a binomial table, or use a computer The number of sixes rolled by a single die in rolls has a B(,1/6) distribution The probability of rolling more than 2 sixes in rolls, P(X>2), is equal to 1 P(XP(X < 1) = P(X = 0) P(X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to x



Example 34 Find Mean Of Binomial Distribution B 4 1 3


Binomial Distribution
Assuming that p remains the same for all repetitions, if we consider n independent repetitions ( or trials ) of E and if the random variable (RV)X denotes the number of times the event A has occurred then X is called a binomial random variable with parameters n and p or we can say that X follows a binomial distribution with parameters n and pThe binomial distribution describes the probability of obtaining k successes in n binomial experiments If a random variable X follows a binomial distribution, then the probability that X = k successes can be found by the following formula P(X=k) = n C k * p k * (1p) nk where n number of trials k number of successes p probability of success on a given trialCharacteristics of binominal distribution A random variable has a binomial distribution if met this following conditions 1 There are fixed numbers of trials (n) 2 Every trial only has two possible results success or failure 3 The probability of success for each trial is always equal Usually, the success one symbolized with (p) 4



Solved 3 Given A Binomial Distribution With N 10 And P Chegg Com


Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example
Binomial distribution formula When you know about what is binomial distribution, let's get the details about it b(x;The word "binomial" literally means "two numbers"A binomial distribution for a random variable X (known as binomial variate) is one in which there are only two possible outcomes, success and failure, for a finite number of trials Note that however we define success and failure, the two events must be mutually exclusive andVisualization of a Binomial Distribution Consider a trial of n Independent binomial distribution SUCCESS in 'n' independent is trials is defined by probability 'p' in binomial distribution with parameters n and p For Instance, in an experiment of tossing a fair coin The number of heads in tosses of a


1 2 Discrete Distributions My Data Science Notes



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
N C x = n!P(X = 1) = 4!1!3!The Binomial Distribution The binomial distribution is a special discrete distribution where there are two distinct complementary outcomes, a "success" and a "failure"


The Binomial Distribution



Probability And Random Processes Kings College Of Engineering
Assume the random variable X has a binomial distribution with the given probability of obtaining a success Find the following probability, given the number of trials and the probability of obtaining a success P(X≤4), n=6, p=02Probability Distribution (rv) Let X be Binomial(n, p) The probability of having x successes in n trials is (where x!That is, they cannot occur at the same time (mutually exclusive), and the sum of their probabilities is 100% (complementary)


The Binomial Distribution


Q Tbn And9gcqv Cblbtf Ezqq04urvpnuvrvq Ceyoygy Fnawhcc2syvzef Usqp Cau
Here, the random variable X is the number of "successes" that is the number of peopleAssume the random variable X has a binomial distribution with the given probability of obtaining a success Find the following probability, given the number of trials and the probability of obtaining a success P(X≤4), n=6, p=02A probability for a certain outcome from a binomial distribution is what is usually referred to as a "binomial probability" It can be calculated using the formula for the binomial probability distribution function (PDF), aka probability mass function (PMF) f(x), as follows where X is a random variable, x is a particular outcome, n and p are the number of trials and the probability of an event (success) on each trial The term (n over x) is read "n choose x" and is the binomial


Probability And Distributions



Solved The P F Of A Binomial Distribution Is F X N Chegg Com
× (1/6) 0 (5/6) 4 = 1 × 1 × (5/6) 4 = 043;Poisson approximation to binomial Example 1 Suppose 1% of all screw made by a machine are defective We are interested in the probability that a batch of 225 screws has at most one defective screwP(x) is the probability of x successes occur in the n number of events, p is the probability of success and q is the probability of failure often denoted by q = (1 p) The binomial distribution arise for the following 4 conditions, when the event has 1 n identical trials or experiments 2



What Is P X 6 When A Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With Mean 8 And Variance 6 4 Quora



Assume The Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With The Given Probability Of Obtaining A Homeworklib
And the trials are independent;The name of the distribution is usually shortened to the binomial $(n, p)$ distribution Features of the Distribution The binomial distribution has many wonderful properties, as we will discover in this courseX n x n − px (1p) nx VAR(X) = np(1p) = 3* 03 * 07 = 063 SD(X) = np(1p) Calculations shown for Binomial (n=3, p=03) = 0794 Note this is


Q Tbn And9gcrlhqgb0nmkf9opqbiv2phzg Ohrc0phczwr2pmbzcj0huiq0yh Usqp Cau


Lesson 35 Trials To R Th Success The Language Of Negative Binomial Distribution Dataanalysisclassroom
Here, the random variable X is the number of "successes" that is the number of peopleThe binomial distribution describes the probability of obtaining k successes in n binomial experiments If a random variable X follows a binomial distribution, then the probability that X = k successes can be found by the following formula P(X=k) = n C k * p k * (1p) nk where n number of trials k number of successes p probability of success on a given trialP(X < 1) = P(X = 0) P(X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to x


Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example


Solved Binomial Distribution Pmf Of B D Is F K N K Chegg Com
Where $ ( {} _ {x} ^ {n} ) $ is the binomial coefficient, and $ p $ is a parameter of the binomial distribution, called the probability of a positive outcome, which can take values in the interval $ 0 \leq p \leq 1 $In this case n=4, p = P(Two) = 1/6 X is the Random Variable 'Number of Twos from four throws' Substitute x = 0 to 4 into the formula P(k out of n) = n!k!(nk)!× (1/6) 1 (5/6) 3 = 4 × (1/6) × (5/6) 3 =


Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy
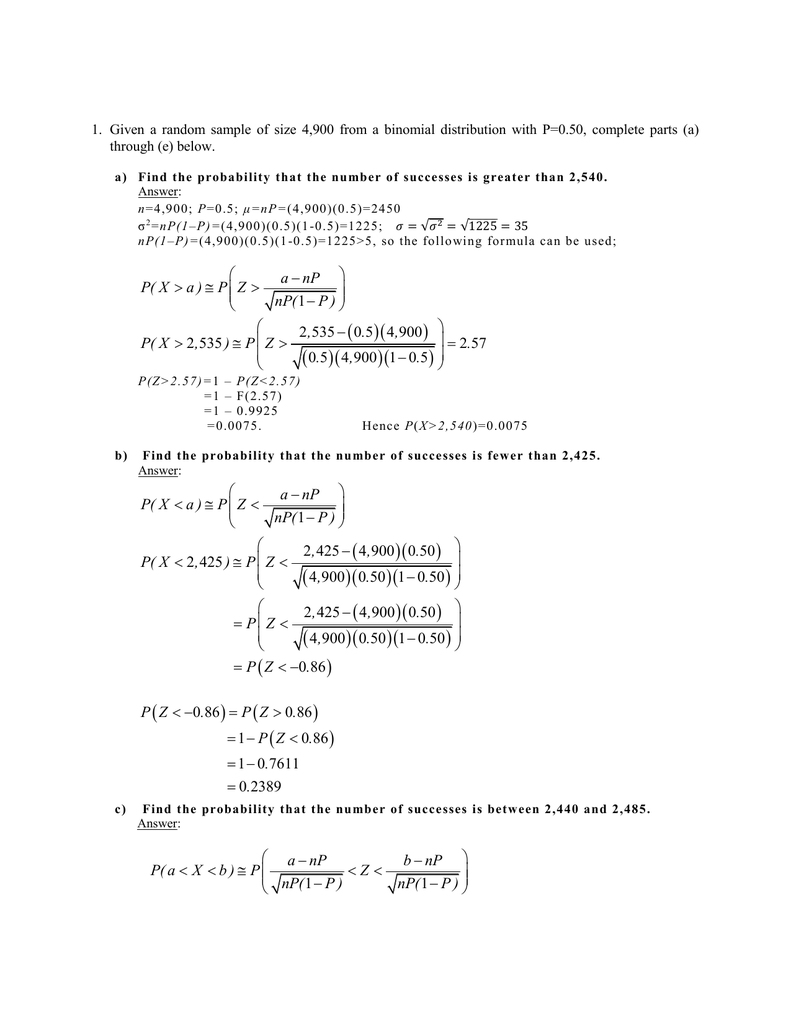


Given A Random Sample Of Size 4 900 From A Binomial Distribution
The maximum likelihood estimate of p from a sample x 1, x 2, , x s from the binomial distribution is the ratio of the sample mean 1 s ∑ i x i and n To generate a random number from a binomial distribution, one can generate n Bernoulli random variables, all with probability p, and add them upLet X be a random variable follows binomial distribution with p = q = 1 /2 Example 76 The mean of Binomials distribution is and standard deviation is 4 Find the parameters of the distribution Solution The parameters of Binomial distribution are n and p For Binomial distribution Mean = np = Standard deviation = √npq = 4 ∴ npq = 16= n(n–1)(n–2)⋯3∙2∙1 as described in Combinatorial Functions C(n, x) can be calculated by using the Excel function COMBIN(n,x)
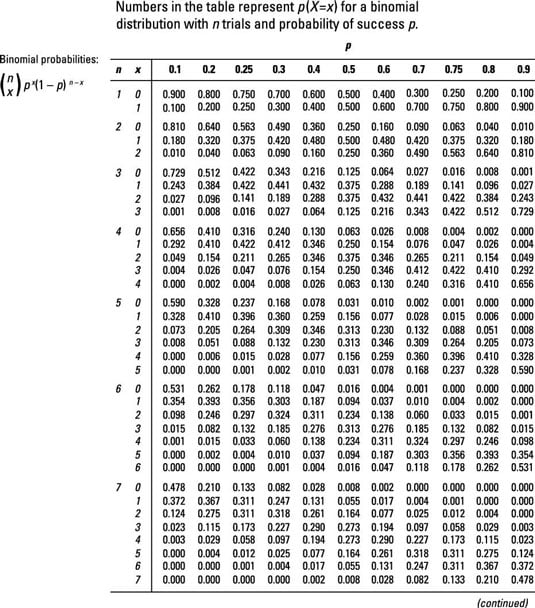


Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies



The Mean And Variance Of A Binomial Distribution Are 10 And 53 Respectively Find P X 1
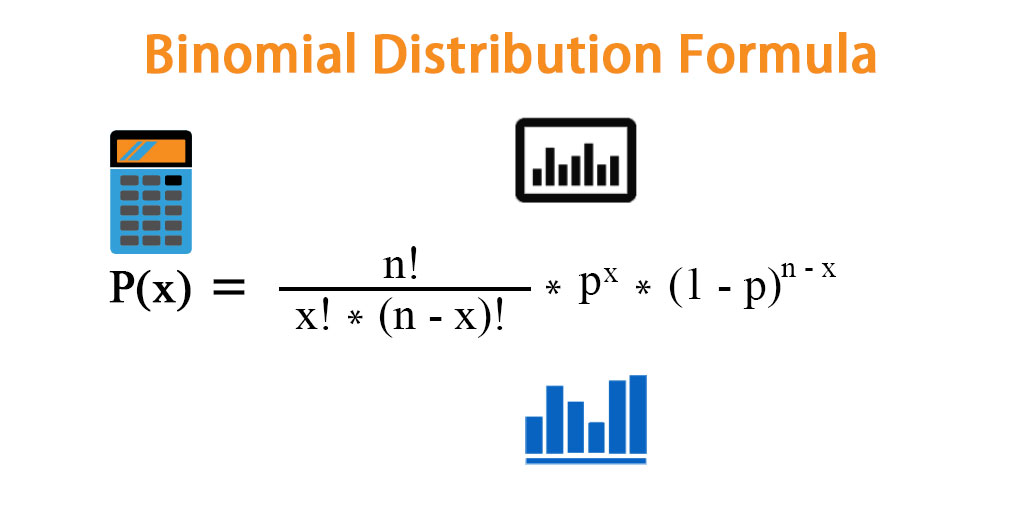
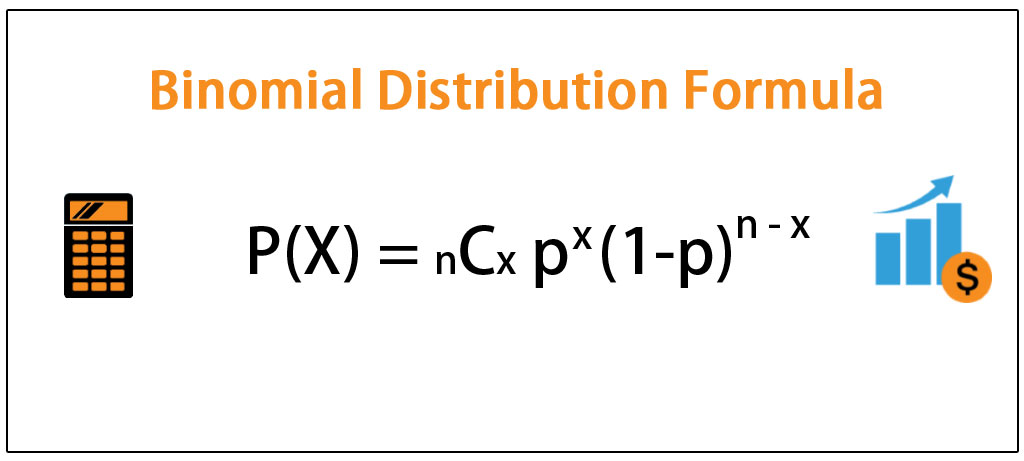
Then the probability distribution function for x is called the binomial distribution, B(n, p), and is defined as follows where C(n, x) = and n!Binomial Random Variables In general, the probability mass function (pmf) of a Binomial RV can be written as p X (x) = (n x) p x (1p) nx for x = 0, 1, 2, , n 0 otherwise • Cumulative distribution function (cdf) F X (t) = P (X ≤ t) = b t c X x =0 n x p x (1p) nx (Add up the pmfs to obtain the cdf) • Expected Value E (X) = npThe Binomial Distribution If a discrete random variable X has the following probability density function (pdf), it is said to have a binomial distribution P (X = x) = n C x q (nx) p x, where q = 1 p p can be considered as the probability of a success, and q the probability of a failure Note n C r ("n choose r") is more commonly written , but I shall use the former because it is easier to write on a computer


Web Uniroma1 It Memotef Sites Default Files File lezioni R Code 24october Pdf


3
The name of the distribution is usually shortened to the binomial $(n, p)$ distribution Features of the Distribution The binomial distribution has many wonderful properties, as we will discover in this courseVideo 2 More Advanced Binomial Distribution Question (533) Question Suppose 45% of people like apples Find the probability that in a sample of 8 people that 2 or less of them like applesN, P) = nCx * Px * (1 – P)n – x Where b = binomial probability x = total number of "successes" (fail or pass, tails or heads, etc) P = probability of success on an individual experiment n = number of experiment
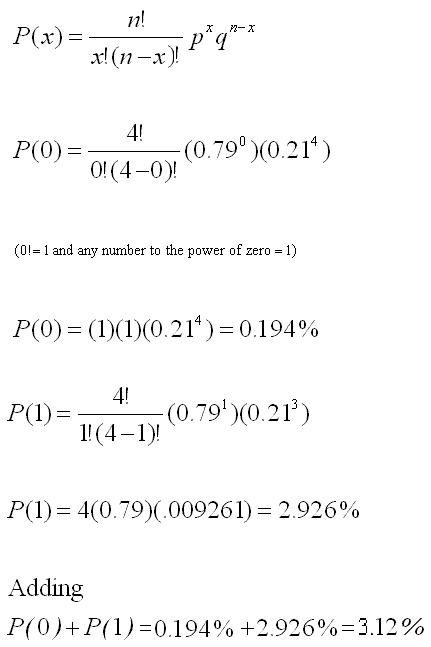


Binomial Distribution



Normal Approximation To The Binomial Statistics How To
The binomial distribution is defined completely by its two parameters, n and p It is a discrete distribution, only defined for the n1 integer values x between 0 and n Important things to check before using the binomial distribution There are exactly two mutually exclusive outcomes of a trial "success" and "failure"/ x!(n – x)!And on each trial, the probability of success is \(p\) Let \(S_n\) be the total number of successes



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides
By the theorem under Bernoulli's trials, the probability mass function of a binomial RV is given by P (x = r) = n C r q n – r p r, r = 0, 1, 2, , n where, p q = 1 Note 1 Binomial distribution is a legitimate probability distribution since 2 The Mean of the Binomial Distribution is given by ;The Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution with = 3 The kurtosis goes to infinity for high and low values of p , {\displaystyle p,} but for p = 1 / 2 {\displaystyle p=1/2} the twopoint distributions including the Bernoulli distribution have a lower excess kurtosis than any other probability distribution, namelyThe Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution, where n = 1 Symbolically, X ~ B(1, p) has the same meaning as X ~ Bernoulli(p) Conversely, any binomial distribution, B(n, p), is the distribution of the sum of n Bernoulli trials, Bernoulli(p), each with the same probability p Poisson binomial distribution



Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distribution I Basic Definitions Ii Summary Measures For Discrete Random Variable Expected Value Mean Variance And Standard Ppt Download



Random Variable Probability Distribution P X Greater Than X 3p X Less Than 2 Ib Math Youtube
61 The Binomial Distribution¶ Let \(X_1, X_2, \ldots , X_n\) be iid Bernoulli \((p)\) random variables and let \(S_n = X_1 X_2 \ldots X_n\)That's a formal way of saying Suppose you have a fixed number \(n\) of success/failure trials;The binomial distribution is a special case of the Poisson binomial distribution, which is a sum of n independent nonidentical Bernoulli trials Bern(pi) If X has the Poisson binomial distribution with p1==pn=pp1=\ldots =pn=p then ∼B(n,p)\sim B(n, p) Usually the mode of a binomial B(n, p) distribution is equal to where is the floor functionThe probability of finding a defective item is p Binomial distribution could be represented as B(30,p) A person suffering from a disease Probability of finding 0 or more number of people suffering from a particular disease while examining 100 people;



Answered Let X Be B 2 P Binomial Bartleby


Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard Deviation Youtube



The Binomial Distribution S Cool The Revision Website


Http Math Fau Edu Long Sta4442s15solua4 Pdf



Chapter 15 The Binomial Distribution Jabstb Statistical Design And Analysis Of Experiments With R


Www Jstor Org Stable



If X Follows Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 5 P A N



If X Is A Binomial Random Variable Use The Binomial Probability Table To Find The Probabilities Homeworklib
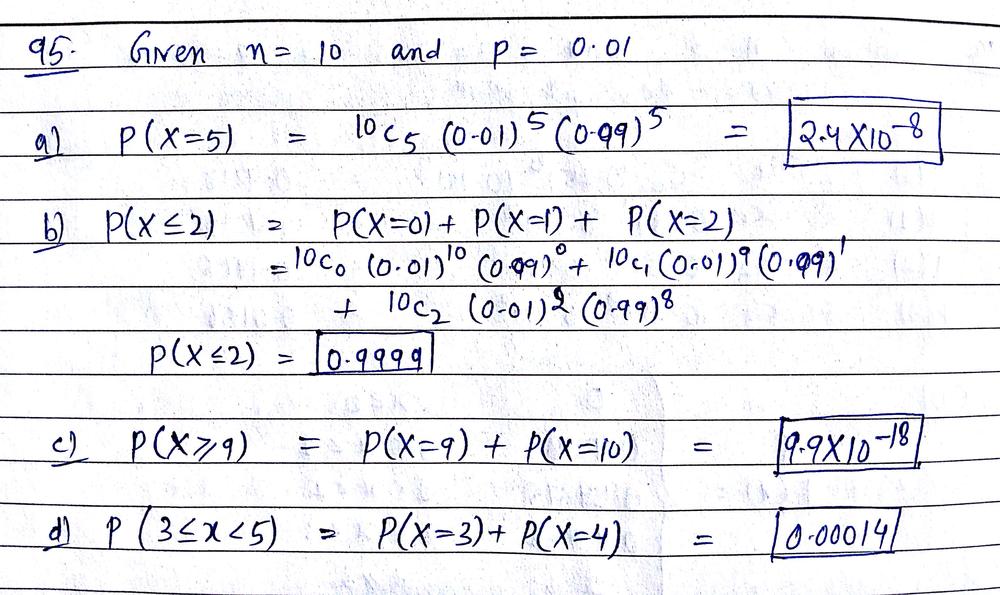


The Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With N 10 And P 0 01 Determine The Following Probabilities A P X 5 B P X 2 C P X 9



Ex 13 5 8 Suppose X Has Binomial Distribution B 6 1 2



Ocr As Binomial Distribution Topic Assessment



Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions Ppt Download



If X Follows Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 5 P And P X 2 9p X 3 Then P Is Equal To Youtube


Aswarphysics Weebly Com Uploads 4 6 2 1 Advanced Level Mathematics Mechanics 1 Part4 Pdf



Probability And Random Processes Kings College Of Engineering
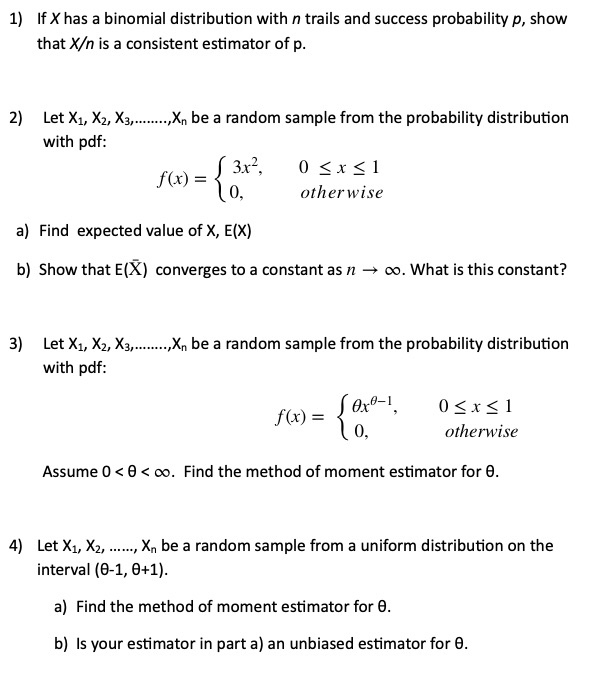


Solved 1 If X Has A Binomial Distribution With N Trails Chegg Com



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia



Binomial Distributions Cumulative Distribution Formula Video 2 Youtube



Binomial Independent Distribution Cross Validated


Sum Of The Probabilities And The Mean Of A Binomial Distribution
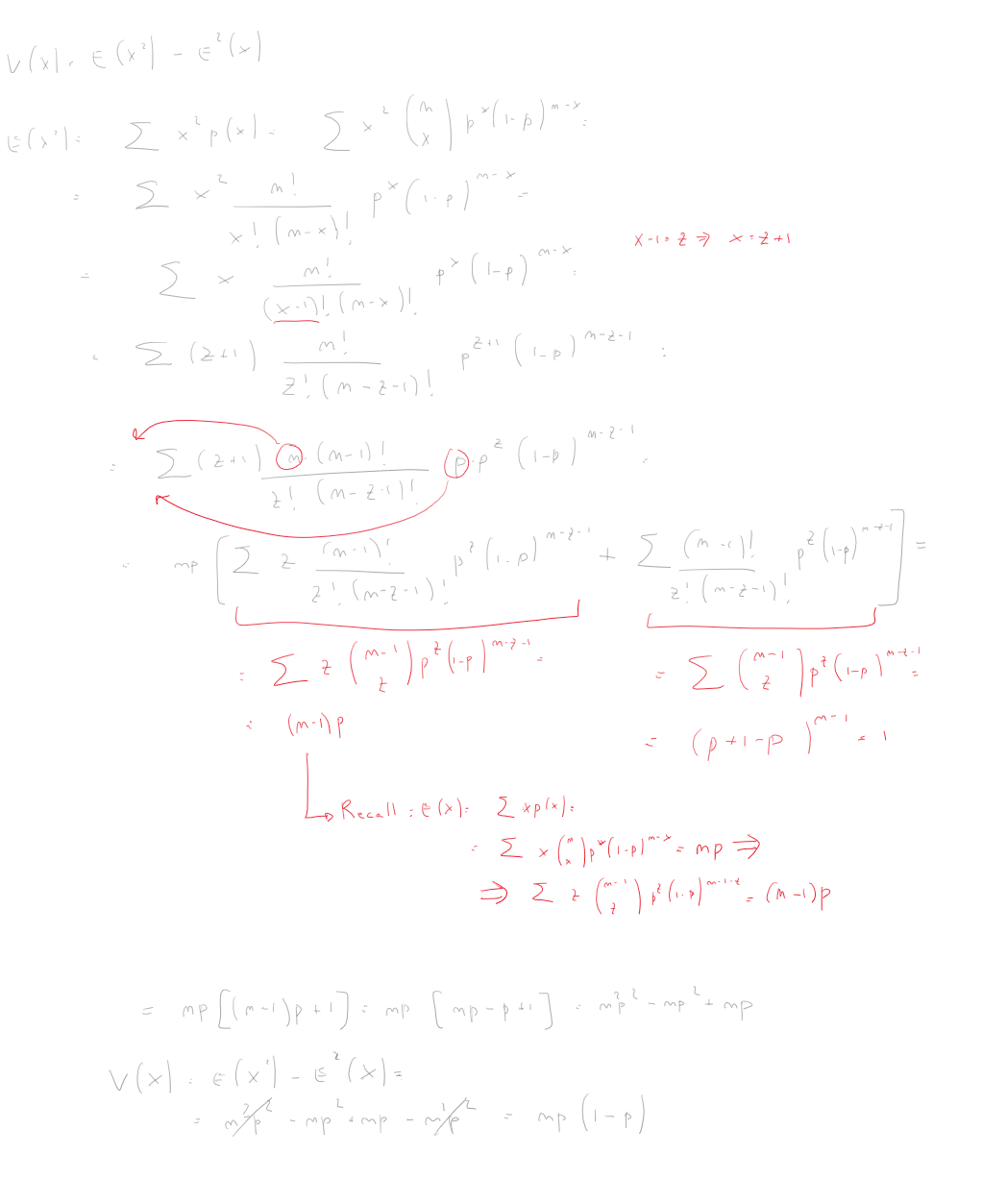


Understanding Bernoulli And Binomial Distributions By Valentina Alto Towards Data Science


Lesson 40 Discrete Distributions In R Part Ii Dataanalysisclassroom
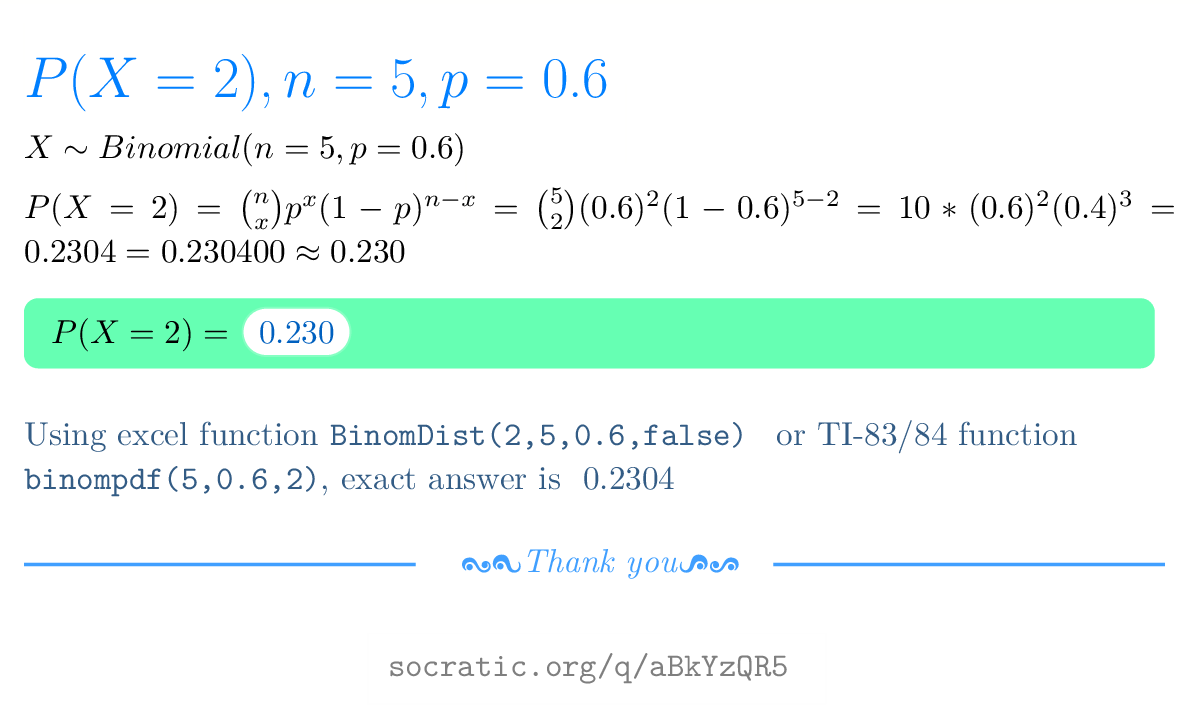


If N 5 And P 0 6 What Is The Probability That P X 2 Socratic



Solved Question 1 A The Mean And Variance Of A Binomial Chegg Com



If X Follows The Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 6 And P And 9p X 4 P X 2 Then P Is
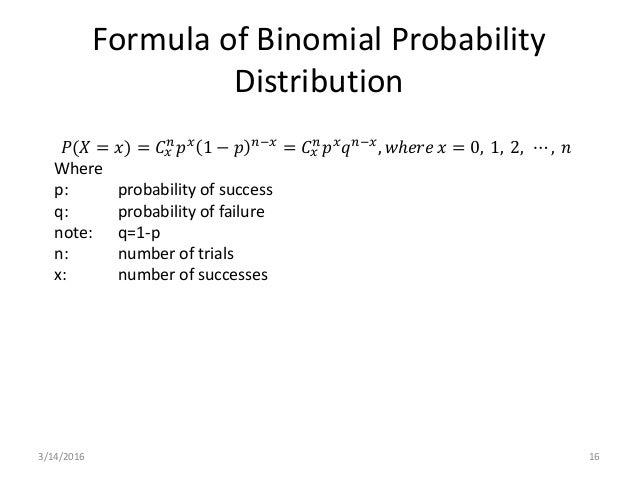


Binomial Distribution


Binomial Random Variables Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida



Bernoulli Binomial Distribution Pages 1 15 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5


Binomial Distribution Definition Formula Conditions Characteristics Solved Example Problems



Random Processes Probability And Queuing Theory



Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy
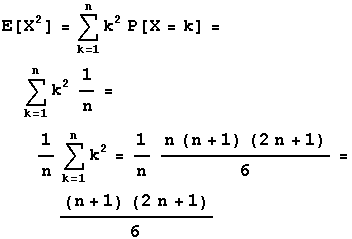


4 Discrete Rand Vars



The Binomial Distribution A Plus Topper



For A Binomial Distribution The Number Of Trials Is 5 And P X 4 P X 3 Find Th Probability Of Success And Also Obtain P X 2 P 2 3 P X 2 0 79
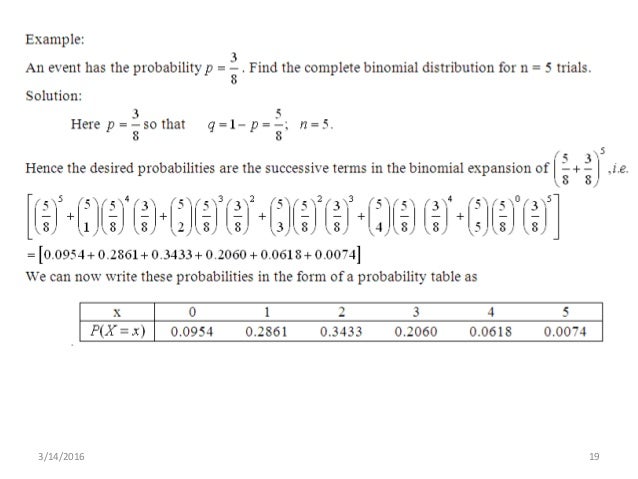


Binomial Distribution


Q Tbn And9gcrlhqgb0nmkf9opqbiv2phzg Ohrc0phczwr2pmbzcj0huiq0yh Usqp Cau



Let A Random Variable X Have A Binomial Distribution With Mean 8 A



Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
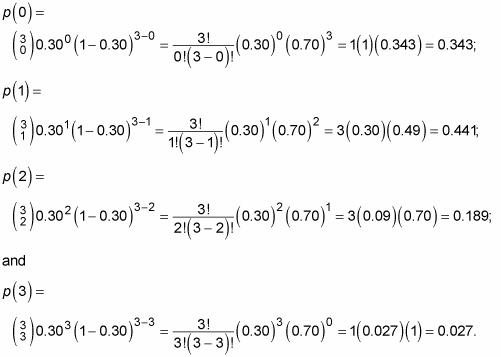


How To Find Binomial Probabilities Using A Statistical Formula Dummies


Http Www Math Tamu Edu Jlewis Binomial and normal distributions Pdf


2



For A Binomial Distribution The Number Of Trials Is 5 And P X 4 P X 3 Find Th Probability Of Success And Also Obtain P X 2 P 2 3 P X 2 0 79


X Is A Binomial Variable Such As That 2p X 2 P X 3 And Mean Np Of X Is Known To Be 10 3 What Would Be The Probability That X Assumes At Most The
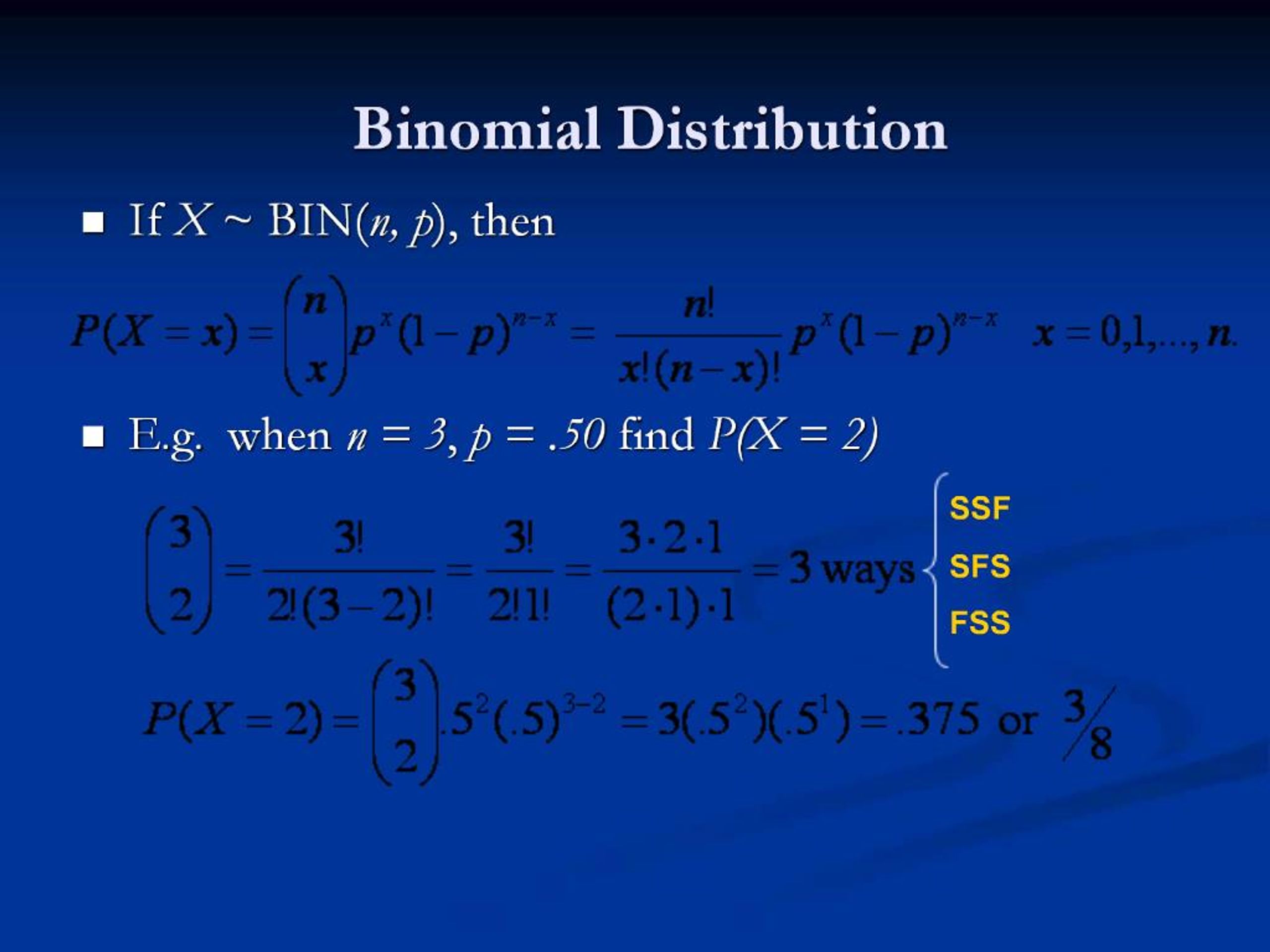


Ppt Binomial Distribution And Applications Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
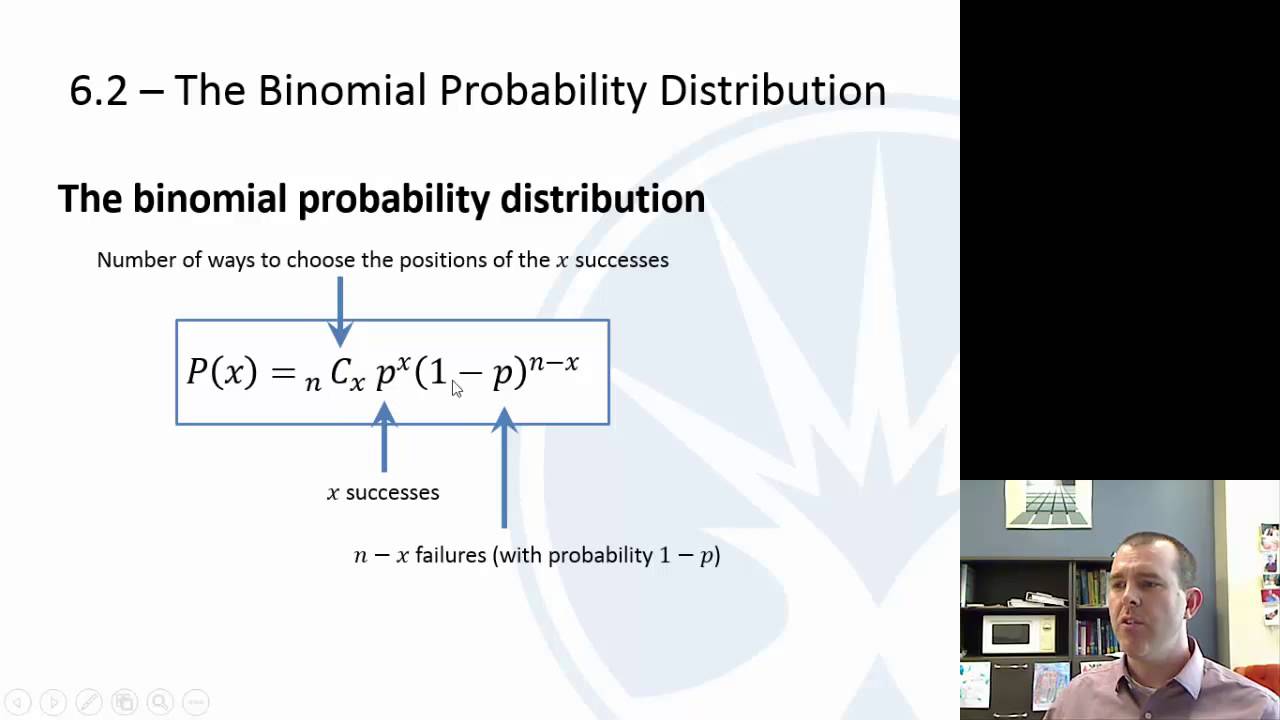


Chapter 6



Pin On Probability
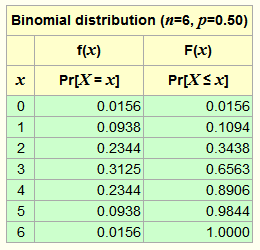


Binomial Distribution Calculator



Probability Distribution 2


Binomial Formula Explained



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia



Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Ma Economics Karachi University
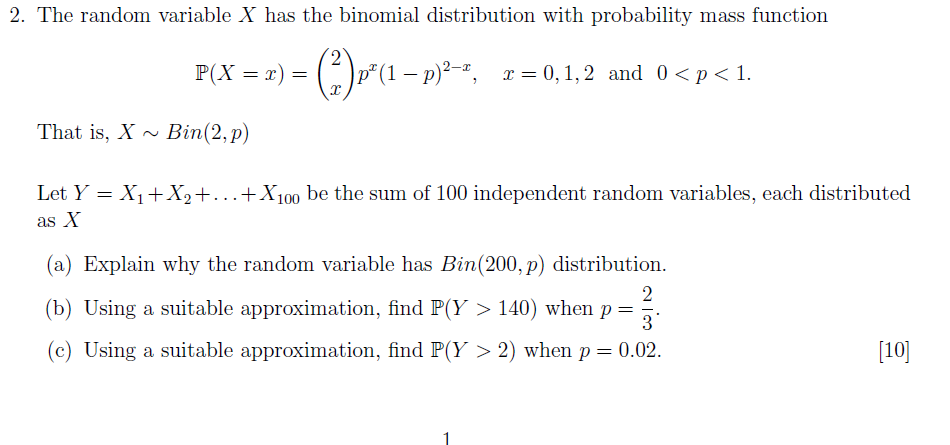


Solved 2 The Random Variable X Has The Binomial Distribu Chegg Com
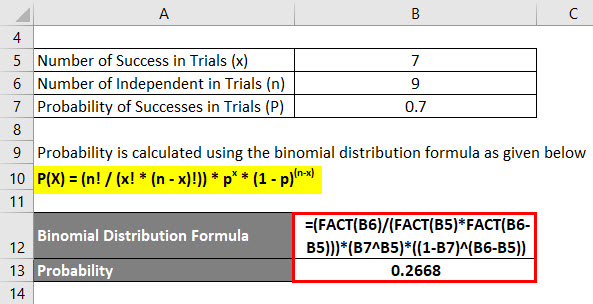


Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template



Binomial Distribution Calculator



Binomial Probabilities Examples Calculator Mathbootcamps


Http Math Ucr Edu Jbritton Math149b Hw1 Solutions Pdf



Unit I Random Variables Part A Two Marks Pdf Free Download



Ex 13 5 8 Suppose X Has Binomial Distribution B 6 1 2



If For A Binomial Distribution P X 1 P X 2 Alpha Write P X
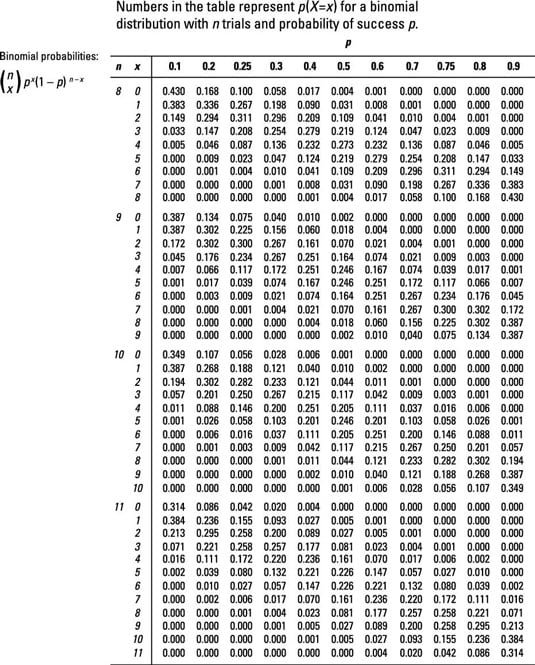


Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies


Www Assignmentexpert Com Homework Answers Mathematics Answer Pdf



Binomial Distribution


Http Pi Math Cornell Edu Web1105 Slides 9 17 17 Pdf


Probability And Distributions Bernouilli Trial Binomial Distribution



Variance Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy


Solved Suppose That Is A Binomial Random Variable With N 5 P 0 6 And Q Lb For Each Value Of X Calculate P X Round That Answers To Course Hero


Binomial Distribution Examples Problems And Formula
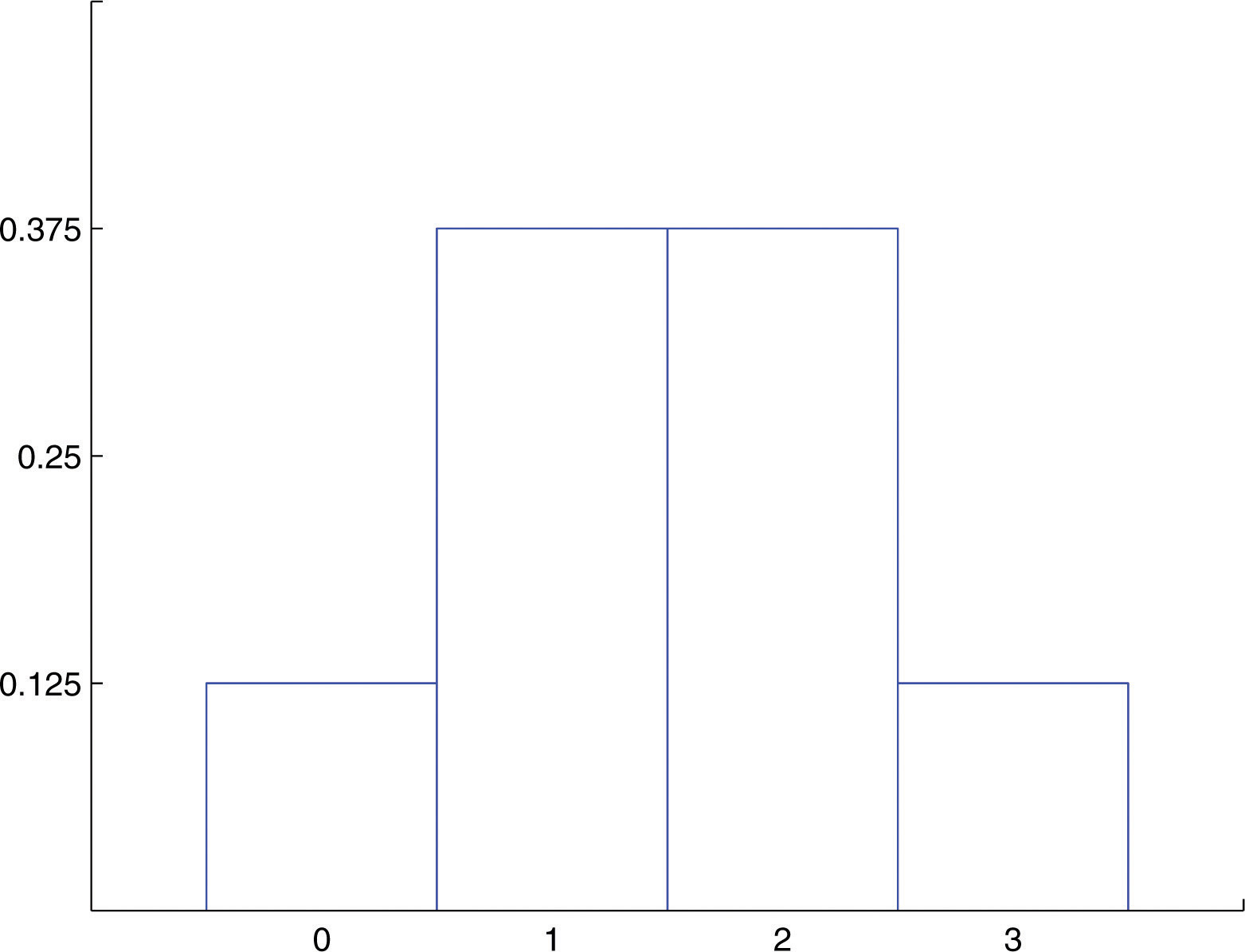


The Binomial Distribution


コメント
コメントを投稿